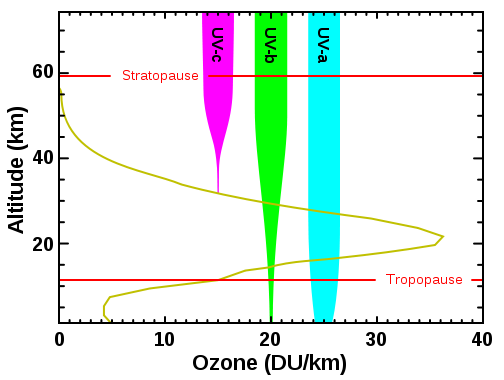
Ozone layer concentration (the yellow-green
curve) is typically only a few parts per million and peaks
near 25 km altitude. UVC (magenta) in
entirely screened out by ozone by 35 km altitude. Most
of the UVA (blue) reaches the ground but is the least damaging
type of UV radiation. It is the UVB (green) that can
cause sunburn and genetic damage eventually resulting in
things like cancer with prolonged exposure. Some UVB
reaches the surface. Thinning of the ozone layer would
allow more UVB to reach the surface which would result in
increased rates of skin cancer, cataracts, and other problems.
Beneficial and harmful effects of exposure to UV light
Exposure to UVB radiation induces the production of vitamin D in the skin. Vitamin D is necessary for good bone health, proper functioning of the immune system. Some have suggested it offers protection from high blood pressure and from cancer. Our bodies can only produce a limited amount of vitamin D from UVB and, for most Caucasians, only a few minutes of sunlight exposure at midday are sufficient (see "Make Vitamin D, Not UV a Priority" from the Skin Cancer Foundation). Diet should be the main source of vitamin D.
Overexposure to UVB radiation can cause sunburn and some forms of skin cancer. UVA and UVB accelerate aging of the skin and destroy vitamin A in the skin. UVA suppresses the immune system, UVB can cause direct damage to DNA. High intensities of UVB light are hazardous to the eyes. Plastic eyeglass lenses offer more protection than glass lenses; polycarbonate lens apparently absorb most of the UV light. High altitude mountain climbers are exposed to higher than average levels of UV radiation, both because there is less filtering by the air overhead and because light can be reflected off ice and snow on the ground (climbers often wear wrap-around glasses with side protection).
Black light
(from the Wikipedia article cited above and a 2nd Wikipedia article on Black light)
If you've ever seen a UV light source, it was probably a "black light." A black light is a lamp that emits UVA light but very little visible light. Black lights are often used to observe fluorescence. If the bright visible light produced by the bulb weren't filtered out it would drown out the weaker light from fluorescence.
The first black lights were made using an ordinary incandescent bulb (a clear glass bulb with a tungsten filament) as shown in the figure below (source).
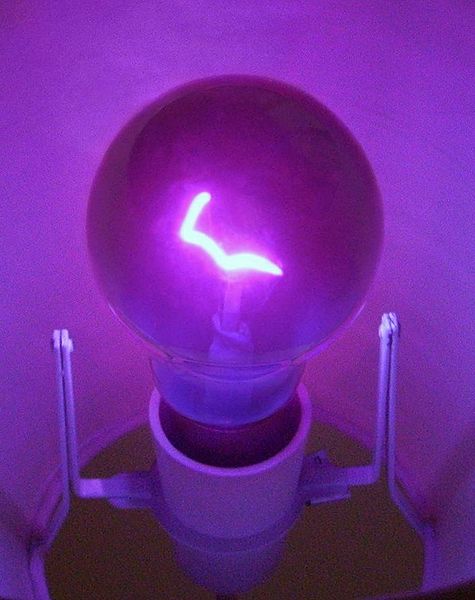

"Wood's glass," a deep bluish-purple glass that filtered out all the light except for UV, is used instead of clear glass (to the human eye the bulb filament would appear magenta and not white as shown in the photograph). This is a very inefficient way of producing UV light. Only about 0.1% of the light produced by the bulb is UV. Because the remaining light is absorbed by the glass, these bulbs can get very hot.
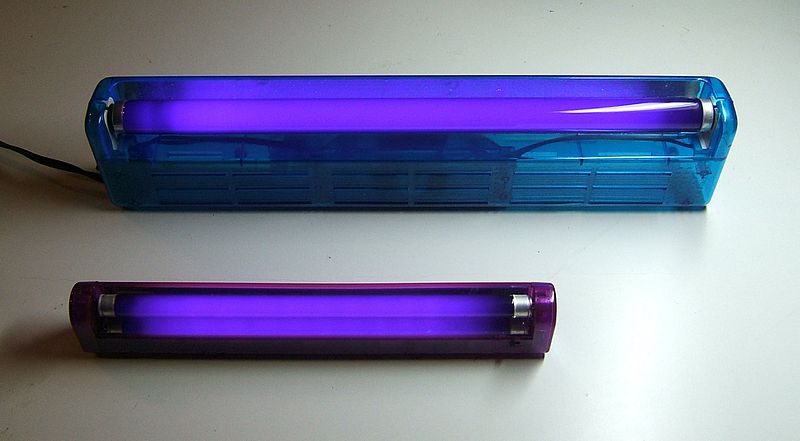
Black light bulbs are often constructed in the same fashion as normal fluorescent lights except that they use a different phosphor on the inside surface of the bulb, one that emits UVA light instead of visible light. Additionally purple glass is used to absorb and block almost all of the visible light above 0.4 μm (source of the photographs below).
These bulbs have a deep purplish-blue color; you are seeing the small amount of visible light these bulbs produce, not the UVA light. The graph above at right shows the relative amounts of UVA and visible light produced by a fluorescent black light bulb. The larger peak, labelled 1, is the invisible UVA light emitted by the bulb. The much smaller peak, 2, is the visible light emitted by the bulb that you are able to see.
Some UV fluorescent bulbs, used to attract insects in "bug zappers," use plain glass instead of purple glass (the zzz2011Viatek BZ02G Indoor/Outdoor Bug Zapper is shown below)
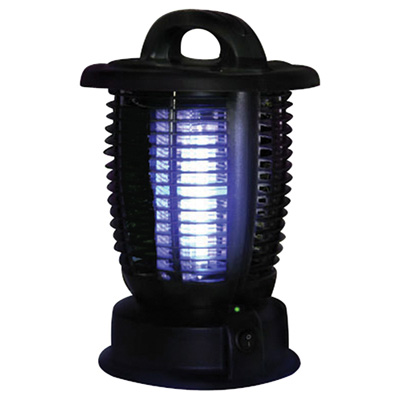

They appear light blue to the naked eye.
The wikipedia article states "The weak output of black light, is not considered sufficient to cause DNA damage or cellular mutations in the way that direct summer sunlight can, although there are reports that overexposure to the type of UV radiation used fro creating artificial suntans on sunbeds can cause DNA damage, photoaging (damage to the skin from prolonged exposure to sunlight), toughening of the skin, suppression of the immune system, cataract formation and skin cancer." It would seem prudent to limit exposure to black light UV and to avoid looking at black light bulbs directly.
Applications
Colorless fluorescent dyes that emit blue light when exposed to UV are added as optical brighteners to a number of white-colored products such as paper and fabrics. The dyes emit blue light when exposed to UV that counteracts any yellow tints that may be present and causes the paper or fabric to appear whiter or brighter.
UV sensitive marks, threads, seals are added to documents such as passports, drivers licenses, and credit cards so that their authenticity can be verified.
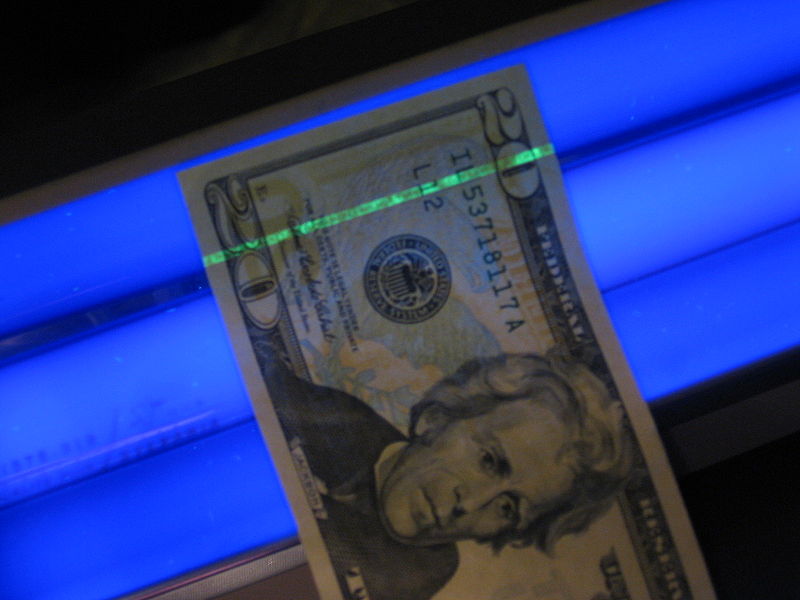

A security thread has been added to the US $20 bill that fluoresces when exposed to UVA light (source of the image above)
UV light can be used to authenticate antiques.
At one time glassware contained uranium which would fluoresce under black light. Peak popularity of this "uranium glass" extended from the 1880s into the 1920s, these objects are now generally considered to be antiques.
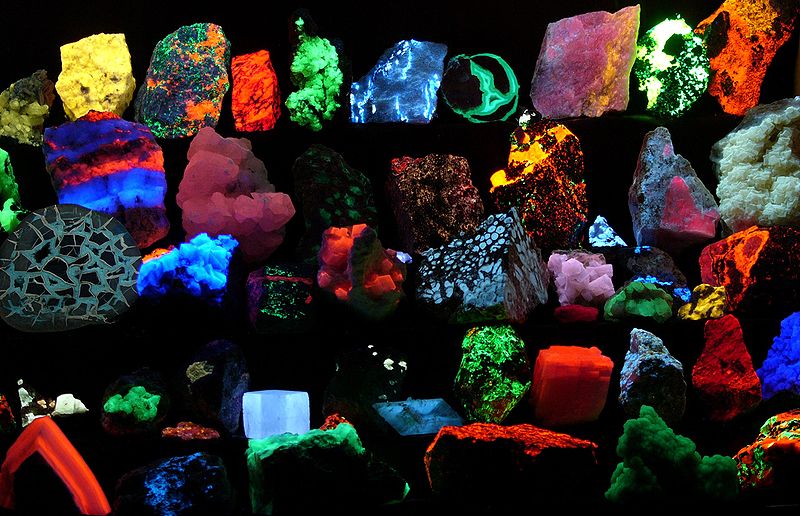
UV light is used in the analysis of certain gems and minerals.

The Arizona bark scorpion is the most venomous species of scorpion in North America. A bite is considered to be life threatening though fatalities are apparently rare (2 fatalities have been recorded in Arizona since 1968, thousands of people are thought to be stung every year in the state according to an article in Wikipedia)
The photograph above at left shows an adult bark scorpion (source of the image and also some advice about what to do if you're stung by a scorpion). An adult is typically 2 to 3 inches long. Scorpions are active at night and will glow green under UV light (black light). I'm not sure what kind of scorpion is shown in the photograph at right (source of the image), I picked it because it was such a nice image.
Beneficial and harmful effects of exposure to UV light
Exposure to UVB radiation induces the production of vitamin D in the skin. Vitamin D is necessary for good bone health, proper functioning of the immune system. Some have suggested it offers protection from high blood pressure and from cancer. Our bodies can only produce a limited amount of vitamin D from UVB and, for most Caucasians, only a few minutes of sunlight exposure at midday are sufficient (see "Make Vitamin D, Not UV a Priority" from the Skin Cancer Foundation). Diet should be the main source of vitamin D.
Overexposure to UVB radiation can cause sunburn and some forms of skin cancer. UVA and UVB accelerate aging of the skin and destroy vitamin A in the skin. UVA suppresses the immune system, UVB can cause direct damage to DNA. High intensities of UVB light are hazardous to the eyes. Plastic eyeglass lenses offer more protection than glass lenses; polycarbonate lens apparently absorb most of the UV light. High altitude mountain climbers are exposed to higher than average levels of UV radiation, both because there is less filtering by the air overhead and because light can be reflected off ice and snow on the ground (climbers often wear wrap-around glasses with side protection).
Black light
(from the Wikipedia article cited above and a 2nd Wikipedia article on Black light)
If you've ever seen a UV light source, it was probably a "black light." A black light is a lamp that emits UVA light but very little visible light. Black lights are often used to observe fluorescence. If the bright visible light produced by the bulb weren't filtered out it would drown out the weaker light from fluorescence.
The first black lights were made using an ordinary incandescent bulb (a clear glass bulb with a tungsten filament) as shown in the figure below (source).

"Wood's glass," a deep bluish-purple glass that filtered out all the light except for UV, is used instead of clear glass (to the human eye the bulb filament would appear magenta and not white as shown in the photograph). This is a very inefficient way of producing UV light. Only about 0.1% of the light produced by the bulb is UV. Because the remaining light is absorbed by the glass, these bulbs can get very hot.
Black light bulbs are often constructed in the same fashion as normal fluorescent lights except that they use a different phosphor on the inside surface of the bulb, one that emits UVA light instead of visible light. Additionally purple glass is used to absorb and block almost all of the visible light above 0.4 μm (source of the photographs below).
 |
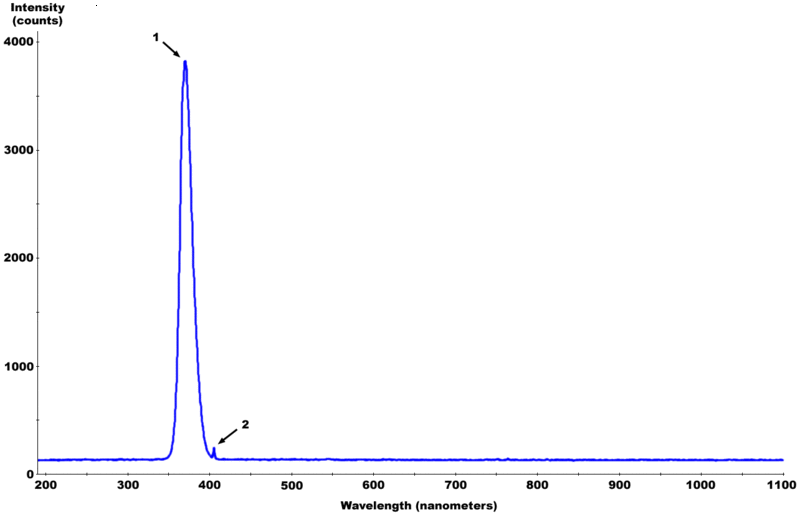 |
These bulbs have a deep purplish-blue color; you are seeing the small amount of visible light these bulbs produce, not the UVA light. The graph above at right shows the relative amounts of UVA and visible light produced by a fluorescent black light bulb. The larger peak, labelled 1, is the invisible UVA light emitted by the bulb. The much smaller peak, 2, is the visible light emitted by the bulb that you are able to see.
Some UV fluorescent bulbs, used to attract insects in "bug zappers," use plain glass instead of purple glass (the zzz2011Viatek BZ02G Indoor/Outdoor Bug Zapper is shown below)

The wikipedia article states "The weak output of black light, is not considered sufficient to cause DNA damage or cellular mutations in the way that direct summer sunlight can, although there are reports that overexposure to the type of UV radiation used fro creating artificial suntans on sunbeds can cause DNA damage, photoaging (damage to the skin from prolonged exposure to sunlight), toughening of the skin, suppression of the immune system, cataract formation and skin cancer." It would seem prudent to limit exposure to black light UV and to avoid looking at black light bulbs directly.
Applications
Colorless fluorescent dyes that emit blue light when exposed to UV are added as optical brighteners to a number of white-colored products such as paper and fabrics. The dyes emit blue light when exposed to UV that counteracts any yellow tints that may be present and causes the paper or fabric to appear whiter or brighter.
UV sensitive marks, threads, seals are added to documents such as passports, drivers licenses, and credit cards so that their authenticity can be verified.

A security thread has been added to the US $20 bill that fluoresces when exposed to UVA light (source of the image above)
UV light can be used to authenticate antiques.
 |
 |
At one time glassware contained uranium which would fluoresce under black light. Peak popularity of this "uranium glass" extended from the 1880s into the 1920s, these objects are now generally considered to be antiques.
UV light is used in the analysis of certain gems and minerals.

(The specimens in this photograph are all
identified here)
The Arizona bark scorpion is the most venomous species of scorpion in North America. A bite is considered to be life threatening though fatalities are apparently rare (2 fatalities have been recorded in Arizona since 1968, thousands of people are thought to be stung every year in the state according to an article in Wikipedia)
 |
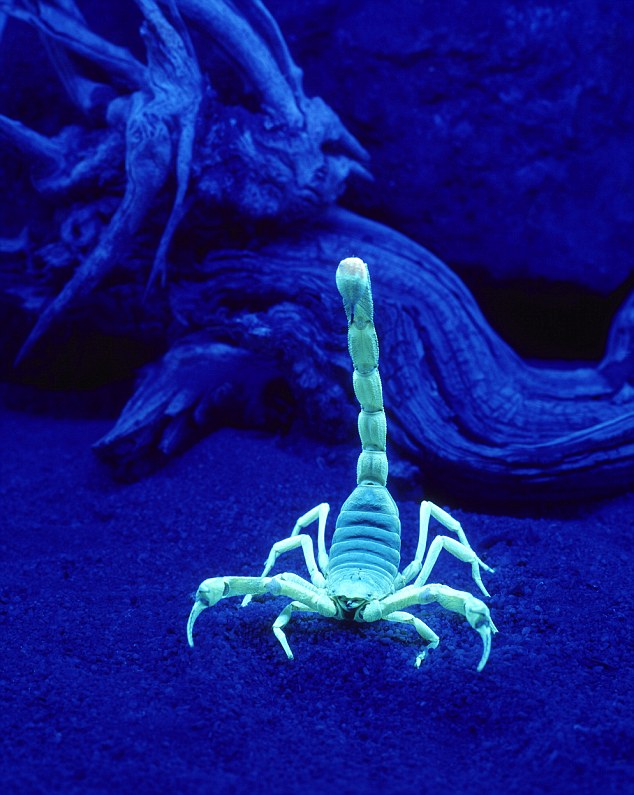 |
The photograph above at left shows an adult bark scorpion (source of the image and also some advice about what to do if you're stung by a scorpion). An adult is typically 2 to 3 inches long. Scorpions are active at night and will glow green under UV light (black light). I'm not sure what kind of scorpion is shown in the photograph at right (source of the image), I picked it because it was such a nice image.