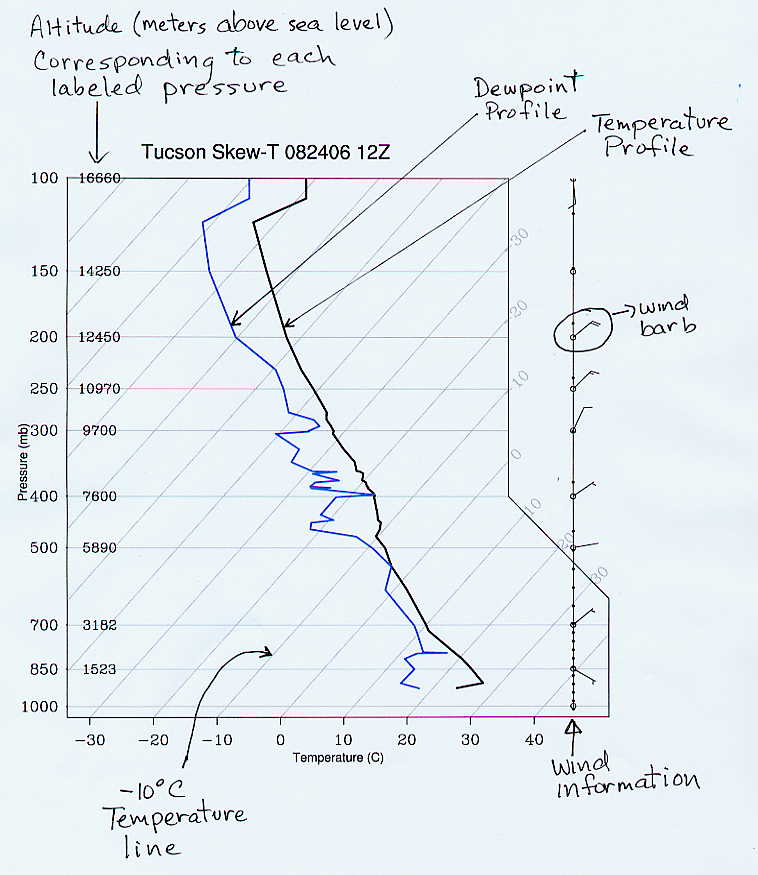
The Skew-T Diagram
The Skew-T diagram gives a "snapshot" picture of temperature, dewpoint, air pressure, and winds in the atmosphere above a particular point on the Earth's surface. The data is measured by launching hydrogen or helium filled balloons carrying weather instrument packages called radiosondes. As the balloon rises, the measurements are transmitted to a ground receiver. Twice a day – at 0000 and 1200 UTC (Universal Coordinated Time) – about 800 radiosondes are launched worldwide, including one from the Tucson airport. (NOTE: 0000 UTC corresponds to 5 P.M. local Tucson time and 1200 UTC corresponds to 5 A.M. local Tucson time. Tucson local time is always 7 hours earlier than UTC.) The measured data is then plotted on a skew-T diagam. Skew-T diagrams are used by meteorologists to help determine atmospheric stability and to assess the possibility for the development of severe thunderstorms.
In this class we are going to use stripped-down, skew-T diagrams to visualize the vertical structure of the atmosphere. This page describes how to read some of the information contained in the diagram. The skew-T diagram shown below was generated for Tucson on August 24, 2006 at 1200 UTC (labeled as 12Z, often 0000 UTC is labeled as 00Z and 1200 UTC as 12Z). The bold black line is a plot of the vertical temperature above Tucson and the bold blue line is a plot of the vertical dewpoint temperature above Tucson. The vertical axis is the air pressure in millibars (mb), and the horizontal lines on the graph are lines of constant pressure. The numbers printed on top of these pressure lines indicate the height above sea level in meters (m) at each of the pressure levels. For example, on this day and time, when the radiosonde balloon reached 5890 m above sea level, the measured air pressure was 500 mb. As expected air pressure must decrease as you move upward in the atmosphere.
The tricky part about reading the skew-T diagram is that the lines of constant temperature are not vertical as in most graphs, but “skewed” at an angle of 45° from vertical. These lines are spaced on the graph every 10° C. To help you see this, the constant temperature lines are labeled on both the bottom and right axes of the plot. For example, at 700 mb (3182 m above sea level), the air temperature above Tucson was 10° C, since the bold, black temperature plot lies right over the 10° C constant temperature line. Now follow the bold, black line upward from there. Notice that the atmospheric temperature drops to the freezing level (0° C) somewhere between 700 mb and 500 mb (3182 m and 5890 m). Continuing upward to where the air pressure is 500 mb, hopefully you can see that air temperature at this point in the atmosphere is approximate -7° C.
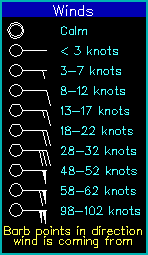
The final bit of information on the skew-T diagram is the wind information shown along the right side of the diagram. The “wind barbs” indicate both the wind speed and wind direction at the corresponding air pressure and altitude. The wind barb points in the direction from which the wind is coming, with respect to standard compass directions. For a wind from the north the barb sticks straight up, from the east the barb points right, from the south the barb points straight down, and from the west the barb points left. For example the circled wind barb indicates that the measured wind at 200 mb was from the northeast. Wind speed is indicated by the line segments and flags attached to the end of the barb. There are long and short line segments. Each long line segment represents 10 knots of wind (there can be up to 4 long line segments). A short line segments represents an additional 5 knots of wind. For example the circled wind barb indicates a wind speed of 20 knots, whereas the wind barb directly below the circled wind barb indicates a wind speed of 15 knots. Each Flag on a wind barb represents 50 knots of wind speed. In the example all of the winds were too light to need a flag. A legend for wind speed is shown below. (By the way a knot is a nautical mile per hour. 1 knot = 1.15 miles per hour).
 |
 |